Are you a Medicare patient enrolled in Upperline Plus?
If yes, call 1-855-669-7843 for 24/7 access to care.
Upperline Health
Augusta
1416 Wainbrook Drive
Augusta, Georgia 30909
Podiatrists at Upperline Health Augusta provide the best foot and ankle care for bunions, arthritis, diabetic foot ulcers and more in Augusta, Georgia and surrounding areas.
Make Appointment
Address
1416 Wainbrook Drive
Augusta, Georgia 30909
Get Directions
Hours
- Monday: 8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- Tuesday: 8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- Wednesday: 8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- Thursday: 8:30 am - 5:00 pm
- Friday: 8:30 am - 12:00 pm
- Saturday: Closed
- Sunday: Closed
Treatment
Upperline Health Augusta in Augusta, Georgia provides foot and ankle care for all patients including adults and children of all ages.
Treatments at Upperline Health Augusta
Foot & Ankle Care
Our foot doctors treat the full spectrum of foot and ankle ailments like skin and nail issues, arthritis, bunions and any problem you may have with your feet.
Wound Care
Our wound care experts deal with all types of non-healing wounds and ulcers. Let us get you healed and back on your feet.
Surgical Treatment
Did you know we are surgeons too? We have some of the nation’s leading surgeons with extensive training and advanced techniques for surgical care.
Chronic Care Management
We help patients manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, chronic kidney disease (CKD), congestive heart failure (CHF), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
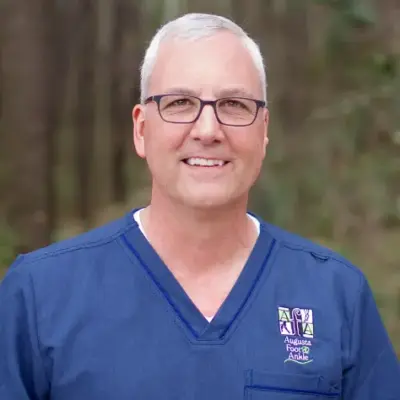
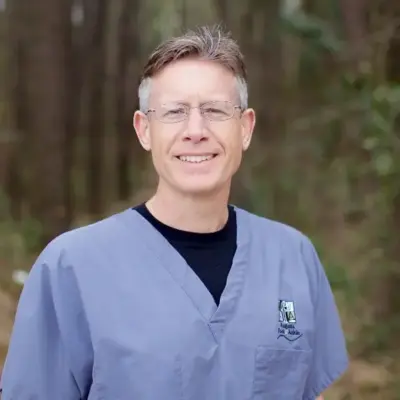
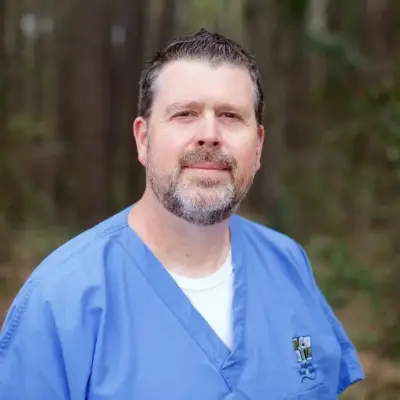
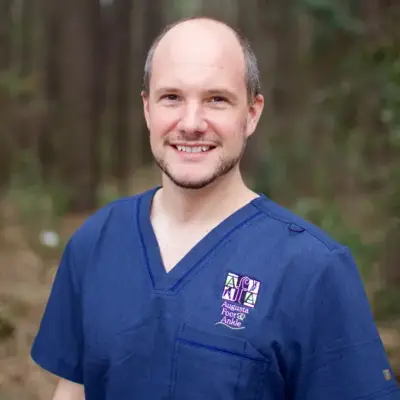
Meet Our Doctors at Upperline Health Augusta
The podiatrists and support team at Upperline Health Augusta in Augusta, Georgia are ready to help you with your foot and ankle conditions.
Preparing for Your Appointment
at Upperline Health Augusta
All new patients should arrive 15 minutes before their scheduled appointment time to complete any necessary paperwork. If your insurance plan requires a referral, please obtain one prior to scheduling an appointment.
What you need to complete the process:
- Patient Name
- Patient Date of Birth
- Patient Address
- Phone Number
- Email Address
- Insurance Provider
- Insurance Plan Name
- Insurance Group ID
- Insurance Member ID